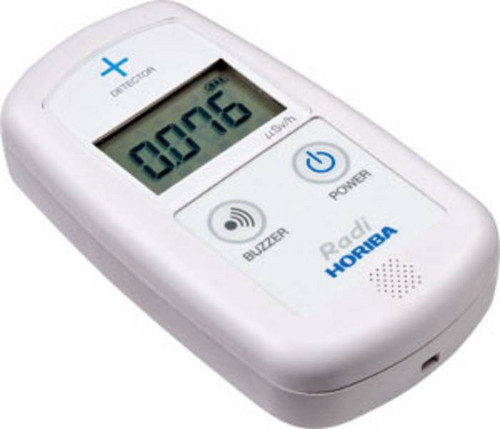
| 검출방식 | scintillation 식 |
|---|---|
| 측정방사선 | γ 선 |
| 감도 | 0.01μSv/h 에 대하여 분당 10count 이상 |
| 상대지시오차 | ±10%이내 |
| 변동율 | 0.1 이하 |
| 에너지범위 | 150keV 이상 |
| 에너지특성 | 0.5~3※1 (150keV~1.25MeV) |
| 유효측정범위 및 표시 | 0.001~9.999μSv/h 디지털 4 항표시(count 수를 μSv/h 로 변환) |
| 샘플링시간 | 60 초 |
| 표시간격 | 60 초의 적산치(이동평균)를 10 초 간격으로 표시 |
| 외형 | 68(W) × 28(D) × 121(H) mm |
| 무게 | 175g(전지무게 제외) |
| 부속품 | 취급설명서、건전지 2 개 |
※1 137Cs(662keV)에 대한 감도를 1 로 했을 경우의 상대감도
※본 기기는 측정 장소에 있어서의 방사선량의 안전성이나 위험성을 판정하는 것이 아닙니다.
자료실
Types of radiation
- Alpha rays (α): Alpha rays are streams of positively charged particles made up of two neutrons and two protons (helium nucleus). In the natural world, alpha rays are given off by radium 226. In air, the particles cannot travel more than a few centimeters.
- Beta rays (β): Beta rays are streams of electrons. In air, the particles can travel several dozen centimeters in a zigzag pattern.
- Gamma rays (γ): Gamma rays, the most penetrating type of radiation, are electromagnetic waves. They can pass through the human body. X-rays that are used in X-ray machines are also electromagnetic waves.
Radiation units
- Becquerel (Bq): The becquerel (Bq) is the unit of radioactivity. The radioactivity of a substance measured in becquerels is the number of its nuclei that decay each second.
- Gray (Gy) and Sievert (Sv): These units express the effect of radiation. The gray expresses the amount of radioactive energy received, while the sievert expresses the effect on a human being. Normally the gray and the sievert are used to express quantities per hour; the units are Gy/h and Sv/h, respectively.