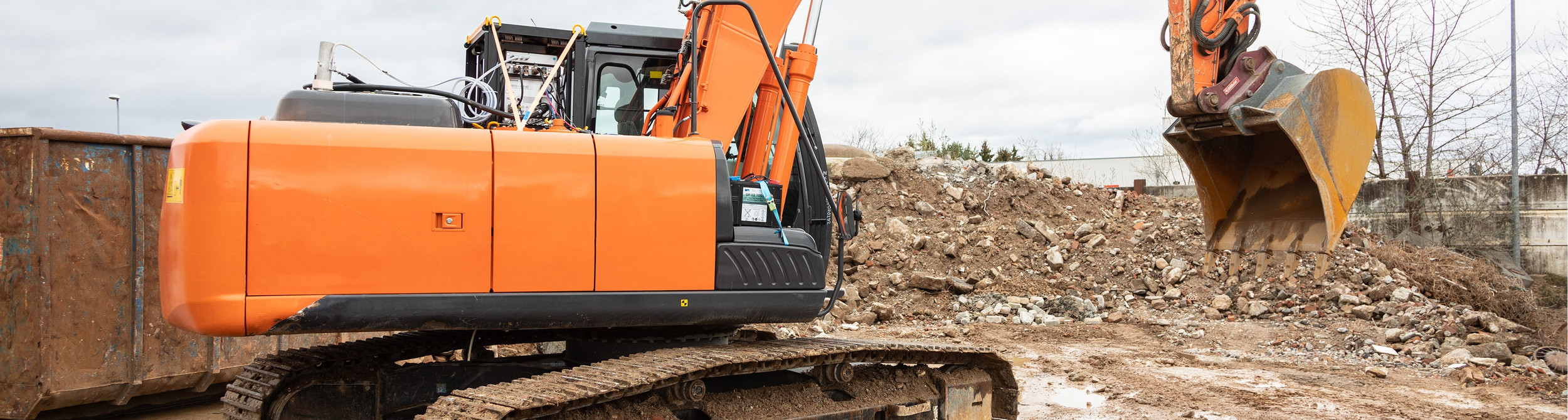

Non-Road Mobile Machinery (NRMM) is a broad term for combustion engine-powered vehicles that seldom if ever use roadways. European NRMM regulations, introduced in 2016 and aimed at engine manufacturers, call for In-Service Monitoring (ISM) using Portable Emissions Measurement Systems (PEMS) for determining Real-World Emissions (RWEs). These new regulations, and others on the near horizon, are changing the way engines and engine-powered vehicles, machinery and equipment are being developed.
Access to, and making sound decisions based on, trustworthy data is your only way to keep costs low and reduce your project risks.
Examples of NRMMs and their categories include portable generating sets (NRG), inland waterway vessels (IWP), all-terrain vehicles with spark ignition engines (ATS), snowmobiles (SMB) and railcars (RLR). There is also a range of engine categories (NRE), based on power output in kW.
All NRMMs are recognised as sources of pollutants and, because of the wide and varied loading NRMM engines experience during normal and abnormal operating conditions, optimum ideal performance is not always achieved; and there is an increase in nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide and dioxide (CO and CO2) and unburned hydrocarbons (HCs) gases.
In addition, there are also numbers of solid particles (PN) and particulate matter (PM), which includes unburnt carbon particles (from the fuel and engine oil) with semi-volatile HCs, sulphate and ash.
NRMM Challenges Video
Regulatory bodies the world over are working to make the type approval process for NRMMs similar to those for heavy-duty vehicles, i.e. PEMS data acquired under increasingly real-world operating conditions is used to complement laboratory testing performed on just the engine and its exhaust after treatment system.
As with heavy-duty vehicles, emissions are reduced through engine design, calibration and exhaust aftertreatment systems. However, unlike HDVs there is far greater diversity with NRMMs, in terms of their physical structures and the environments in which they operate.
Dumper Truck NRMM Emissions
Current regulations require In-Service Monitoring (ISM), as opposed to In Service Conformity (ISC – which is the case for HDVs), and this has applied to some NRMMs, such as tractors, since 2019.
Also, whereas in the past Non-Road Steady Cycle (NRSC) test procedures assessed steady state emission parameters under eight modes, the newer Non-Road Transient Cycle (NRTC) establishes emissions as the engine’s speed and loading change dynamically.
For all your products currently under development you are already seeking that perfect balance between three core parameters: producing equipment that is fit-for-purpose (e.g. power, torque, endurance, reliability etc.), making sure your products are compliant against today’s regulations (which requires investment in engine and exhaust after treatment technologies) and going to market with competitively priced offerings.
The new regulations, and others on the near horizon, are changing the way engines and engine-powered vehicles, machinery and equipment are being developed. The process is extremely iterative with calibration and validation required for the engine, the powertrain system and the machine/equipment as a whole.
Help is at hand, for more information on HORIBA's solutions.
PEMS supports what, for LDVs and HDVs, many call ‘Road to Rig’. The philosophy still stands for NRMM though, as it is all about ensuring real world, in-service loading conditions can be simulated in the laboratory / test cell.
OBS-ONE NRMM
Whereas installing PEMS on a light- or heavy-duty vehicle to record emissions under real world operating conditions is relatively simple, for NRMMs it is far more challenging. There are often severe space constraints and the PEMS often needs to be protected from shock, vibration, dust and the elements. HORIBA’s solution here is a rugged enclosure (RE) to protect its On-board Emissions Measurement System (OBS-ONE), as trusted throughout the automotive sector, from harsh environments. See below, under PEMS.
Accurate PEMS data will become of increasing importance as, in addition to Not-to-Exceed (NTE) limits reducing so too is the ‘conformity factor’, which has to date tolerated generous differences between the laboratory and PEMS methods.
HORIBA have been active in the combustion engine emissions measurement and analysis industry since the 1960s and have grouped together a selection of solutions that can help you capture the data you need to make informed decisions during your R&D work, will save you time and money (through fewer prototypes, for example) and significantly reduce your project risks.
NRMM Solutions Video
Imagine having the world leader in emissions measurement by your side during these challenging times.

A versatile PEMS for engine monitoring under real world operating conditions. The OBS-ONE measures concentrations of emissions (CO, CO2, THC, NOx, NO2), PN, PM, air-to-fuel ratio, exhaust flow rate, GPS data, environmental conditions (atmospheric temperature, humidity and pressure) and calculates mass emissions.
These include:
This product is RDE+ Compatible
HORIBA’s RDE+ is an all-encompassing solution that comprises proven, robust and integrated processes and tools to support your design, development, validation and verification activities

A system that protects the OBS-ONE from harmful shocks and vibrations and which allows accurate emissions measurements in the harshest of environments. The RE also has a WiFi feature to allow remote monitoring and control – which allows the NRMM driver to concentrate on its operation.
These include:
This product is RDE+ Compatible
HORIBA’s RDE+ is an all-encompassing solution that comprises proven, robust and integrated processes and tools to support your design, development, validation and verification activities

EXFM-ONE employs an ultrasonic method for measuring exhaust gas flow rates directly from a vehicle or engine. The unit can be used for various applications such as real time mass measurement of raw exhaust gas.
These include:
Note: The EXFM-ONE may not be suitable for all NRMM exhaust gas flow tests as its maximum flow rate is 10m3/min and the gas temperature limits are 300°C (continuous) and up to 370°C for short bursts.
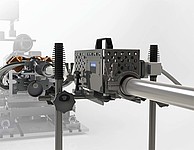
The Pitot Tube Flow Meter, PTFM-1000V2 is a standalone device for measuring the exhaust gas flow rate of a combustion engine. The system uses the tried-and-tested pitot tube principle with high-frequency transducers that ensures pulsations are not missed.
These include:
This product is RDE+ Compatible
HORIBA’s RDE+ is an all-encompassing solution that comprises proven, robust and integrated processes and tools to support your design, development, validation and verification activities

The standalone Dual Pitot Tube Flow Meter, PTFM-ONE DT is used for the measurement of engine exhaust gas flow rates for engine and chassis dyno tests. It consists of a tailpipe attached with two pitot tubes and an interface all housed in a single chassis.
These include:
Note: The PTFM-ONE-DT may not be suitable for all NRMM exhaust gas flow tests as its maximum flow rate is 14.5m3/min.
This product is RDE+ Compatible
HORIBA’s RDE+ is an all-encompassing solution that comprises proven, robust and integrated processes and tools to support your design, development, validation and verification activities
У вас есть вопросы или пожелания? Используйте эту форму, чтобы связаться с нашими специалистами.
